RCI 作者 黎黎 |
COVID-19 已经改变了加拿大经济的方方面面,疫情后,这些变化也将持续下去。
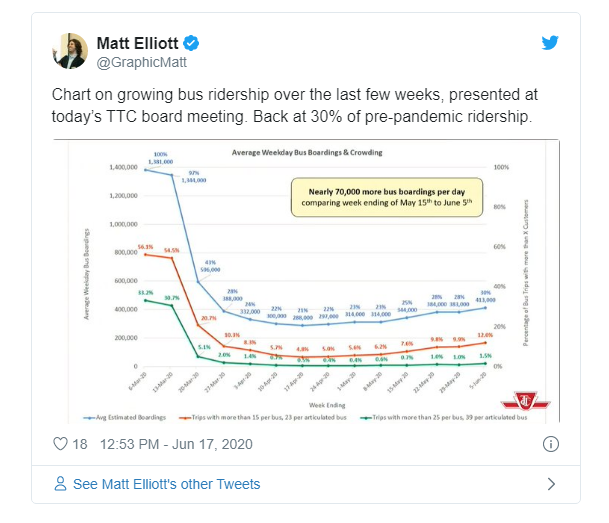
乘公交的人减少
在疫情期间,公共交通的使用人数直线下降,当然这与停摆有关,但是,即使在全部复工后,公共交通的使用人数也不会象以前那么多。
同时,自行车的销量在猛增,选择骑自行车出行的人越来越多。
多年来大受环保人士抨击的汽车,市场的需求也将回升,这是因为,疫情使更多的消费者意识到自己单独出行的安全性。
数据情报公司Validere的商业智能和战略主管 Mark Le Dain 说:这种新趋势完全是有道理的,现在已经没有任何人愿意处在一个有很多人的封闭空间中。
网购大增
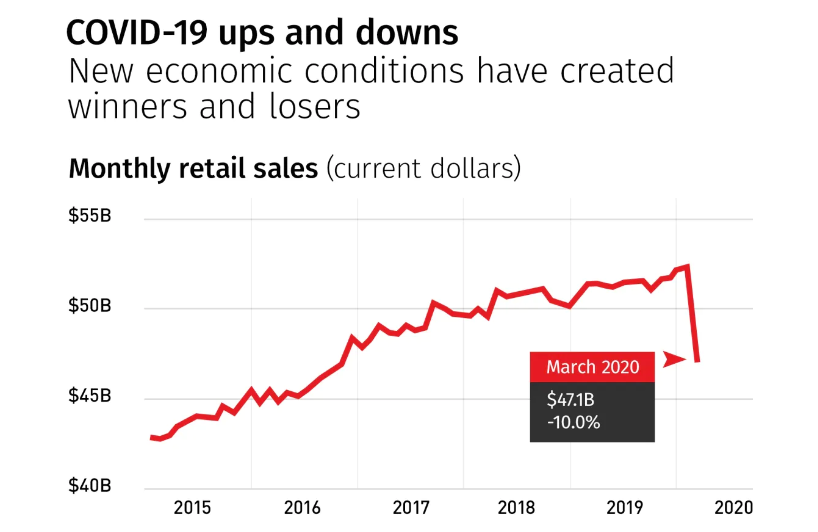
疫情期间,加拿大零售业的表现参差不齐。
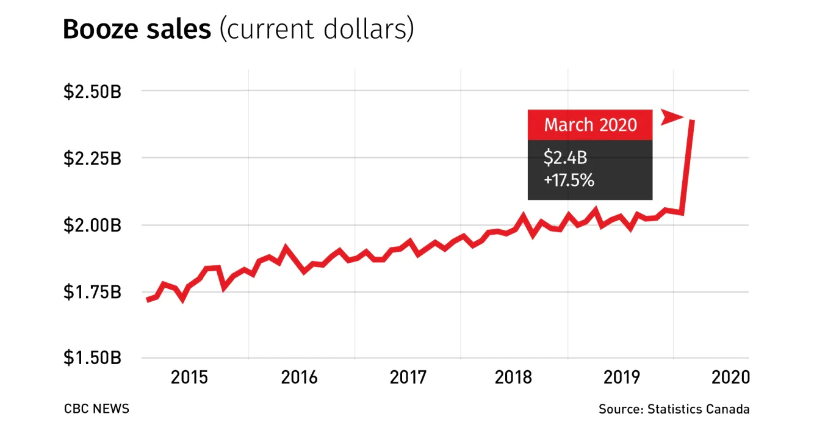
有些商店的销售额飙升,如食品杂货店,但非必需品的商店则受到很大打击。
另一方面,网购领域成为疫情间最大的赢家之一,加拿大 4 月份的网上销售增长了一倍以上,占到加拿大销售总额的 10%,比例大增。
零售业的专家们说,那些在网购平台上落后的商店在疫情种陷入困境,而网购业务强的公司则受冲击较小。
零售顾问布鲁斯·温德说(Bruce Winder)说:疫情正在迫使零售商和供应商们不得不更快地开拓网购业务,消费者现在可以在网上购买到几乎所有东西,商家送货上门,或自己去店外提货,消费者已经越来越习惯这种方便的购物方式。
在家工作
COVID-19 疫情也彻底推动了工作方式的改变,以总部设在渥太华的科技公司 Shopify 为例,该公司最近宣布,现在将根据需要,允许其员工永久在家工作。
多伦多一个网上招聘代理公司的创始人兼企业家詹妮弗·哈格里夫斯(Jennifer Hargreaves)表示:COVID-19 疫情导致了一个积极的趋势,这就是把灵活的工作方式变成了任何希望长期发展的公司的必备条件 。
詹妮弗·哈格里夫斯本人是两个孩子的母亲,她一直在大力提倡公司企业设立灵活的工作方式,从而能有利于更多有孩子的妇女们工作。
她说,让员工远程工作的模式在疫情之前就有了,但这场疫情肯定是加速并普及了这一趋势。
詹妮弗·哈格里夫斯表示:工作场所的非固定性,将有助于公司企业招聘到顶尖的人才,这对公司的发展绝对是有利的,总而言之,这场疫情改变了人们对经济多个方面的思维方式。
(CBC)
How COVID-19 has changed Canada’s economy for the worse — but also for the better
Real estate, retailers and the job market have been hit hard, but there are some reasons for hope
Pete Evans · CBC News · Posted: Jun 23, 2020 4:00 AM ET
Every facet of Canadian life has been changed by the current pandemic, from how and where we live, to how we shop, eat and work. While not all changes have been for the better, COVID-19 could bring about some positive changes to Canada’s economy.
Where we live
The pandemic has certainly wreaked havoc on one of the traditional pillars of Canada’s economy — the housing market.
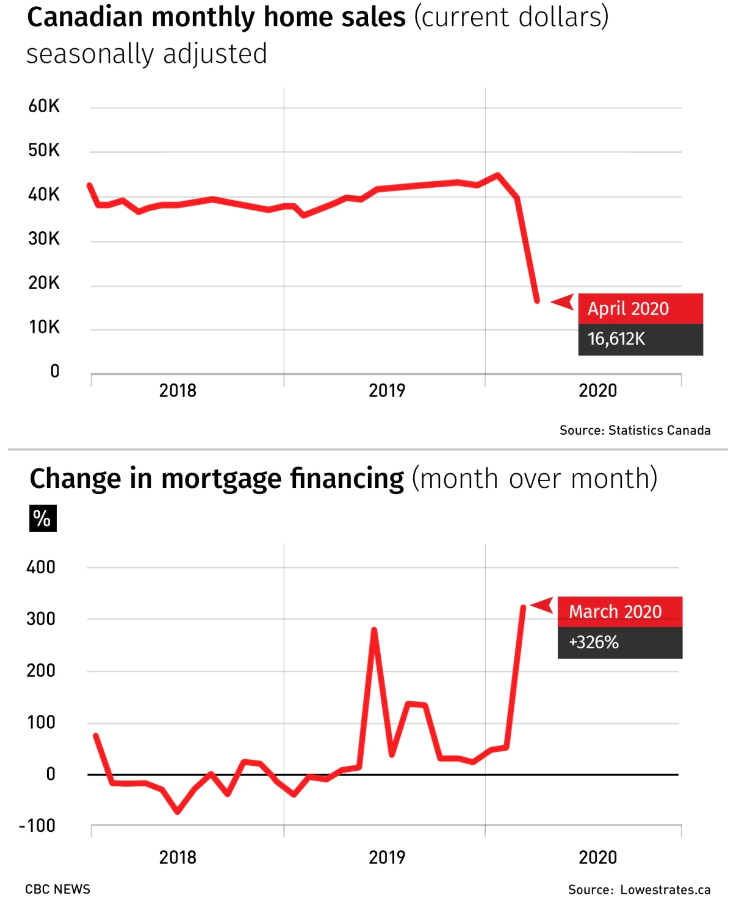
Physical distancing requirements at the onset of the pandemic in March walloped the real estate industry because realtors couldn’t host open houses, and buyers were concerned about the future. This year was the worst April for home sales in almost 40 years, and May was only slightly better.
Realtors are quick to say the slowdown is just a blip, and that demand remains strong. But policy-makers are clearly a little bit concerned. The Bank of Canada is expecting COVID-19 will cause mortgage deliquencies to more than double the peak they hit during the financial crisis of 2009, and Canada’s national housing agency is expecting prices could drop by almost 20 per cent before rebounding starting in 2022, or later.
Lower prices are bad news for sellers, but a slowdown does represent an opportunity for buyers looking to jump to a market that had gotten away from them.
COVID-19 has prompted lenders to cut mortgage rates to record lows, a welcome development for buyers. And those lower rates are helping current homeowners, too.
LowestRates.ca, a comparison website for mortgages, insurance and loans, is seeing interest in refinancing skyrocket right now.
Home sales are plunging, but new buyers are being offered the lowest interest rates on record. Existing owners are refinancing, too. (Joan Dymianiw/CBC)
“We have seen a huge increase in the number of consumers coming to our site to compare rates and see if they can save money by breaking their current mortgage and renewing early or refinancing,” said CEO Justin Thouin.
Where we work
The pandemic is also affecting commercial real estate. It may have started a small shift away from the standard downtown office towers, as many question how much they want to live and work in dense urban areas if they don’t have to.
Public transit use plummeted during the pandemic, and has yet to recover even as the economy has started to reopen.
Toronto’s cash-strapped transit system has missed out on almost $100 million worth of fares, city officials said recently, without a corresponding decline in the costs of running the system.
Bike sales are booming and bike lanes are experiencing a renaissance. But as a partial recovery of oil prices may suggest, even the much-maligned car could see higher demand as consumers opt for the safety and security of their own self-contained travel bubbles.
“This makes perfect sense as no one wants to be in a crowded space currently for themselves or others,” said Mark Le Dain, head of business intelligence and strategy at Validere, a data intelligence firm that advises companies in the energy sector.
How we shop
Retail is another sector of Canada’s economy that has taken the pandemic on the chin. New numbers released last Friday showed retail sales fell by more than a quarter in April, their biggest plunge on record.
While some stores are doing well (business at grocery stores is booming, for example), stores that sell discretionary items are being hit hard for the most part as consumers focus on what they need to get by.
Widespread store closures hit just about every chain, and it looks like many may not recover. Retail stalwarts such as Reitmans and Aldo have sought protection from their creditors in recent weeks, as the pandemic exacerbated the problems they were dealing with already.
Online shopping, on the other hand, is proving to be one of the pandemic’s biggest successes. Online sales more than doubled in April and now make up almost 10 per cent of everything sold in Canada — the biggest proportion on record.
The Canadian chains that ran into trouble were lacking on the e-commerce side, but retail experts say the crisis prompted businesses to dive into the world of retail online.
“Retailers and suppliers have been forced to build out online shopping capabilities at an accelerated rate,” said retail consultant Bruce Winder, author of new book Retail Before, During & After COVID-19. “Consumers now have the convenience of being able to buy almost anything online and have it delivered or use curbside pickup.”
While overall sales are down, some sectors such as grocery stores and alcohol stores are booming. (Joan Dymianiw/CBC)
There’s perhaps no better example of the boom in online selling than the rise of Shopify, the Ottawa-based company that helps real-world stores sell online. Shopify was valued at barely over $1 billion when it went public five years ago. Last month, it passed the Royal Bank of Canada to become the most valuable company in Canada — worth more than $140 billion at last count.
Shopify is a great example of the type of company that could be set to thrive in the post-COVID economy: nimble, innovative and digitally focused.
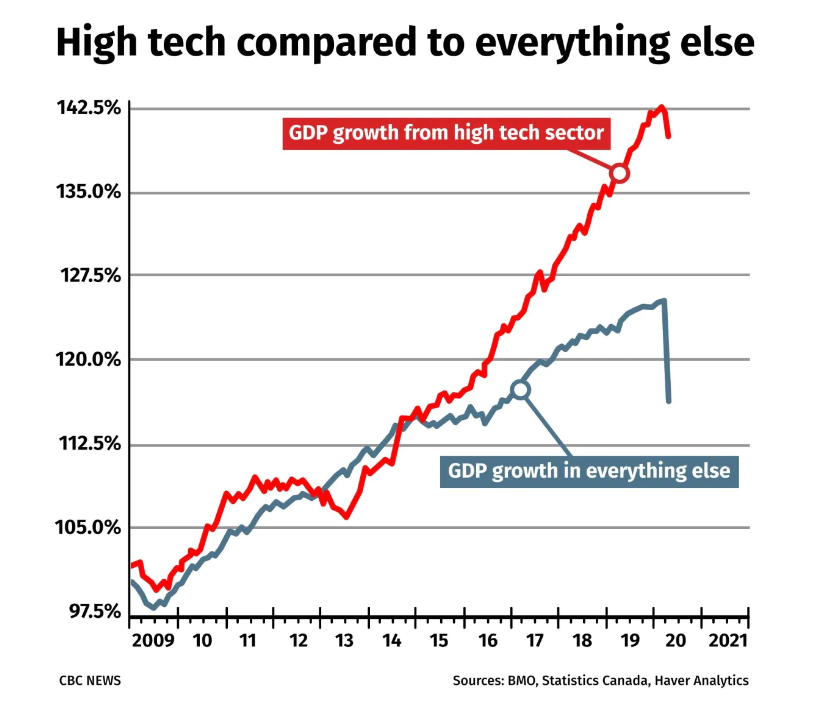
Tech companies like Shopify represent a small but growing part of Canada’s economy. The tech sector has grown twice as fast as the rest of the economy in the last decade, and now makes up five per cent of Canada’s entire GDP, according to the Bank of Montreal.
Canada’s technology sector is now about five per cent of the entire economy, growing much faster than any other part. And while IT has been hit by COVID-19, the impact hasn’t been as dramatic, either. (Scott Galley/CBC)
Even tech hasn’t been immune to the slowdown of COVID-19, but the sector hasn’t plunged by nearly as much as others. The resilience of Canada’s technology sector is an encouraging sign as Canada’s economy tries to reorient itself for the post-pandemic reality.
How we work
The sea change of COVID-19 has impacted Shopify itself, as the company recently announced it will now allow its employees to work from home permanently, should they desire. The company has a stylish headquarters in downtown Ottawa.
Such a move would have been considered unthinkable not too long ago, but the pandemic has hurried along changes in the way Canadians work.
One positive trend emerging from COVID-19 is it has turned flexible work from something that companies used to pretend to care about, into a must-have for any firm hoping to thrive long term, said Jennifer Hargreaves, entrepreneur and founder of recruitment agency tellent.
The shift was underway before COVID-19, but has certainly accelerated during the pandemic, she said.
“This is very much about collaboration and making work work better for everybody,” Hargreaves said.
Instead of trying to fix a broken system, companies hiring top talent today are taking flexibility seriously. “That’s where you’re going to see companies thrive,” she said. “That old way of thinking about the economy is not going to be sustainable.”
https://www.cbc.ca/news/business/covid-economy-changes-1.5618734